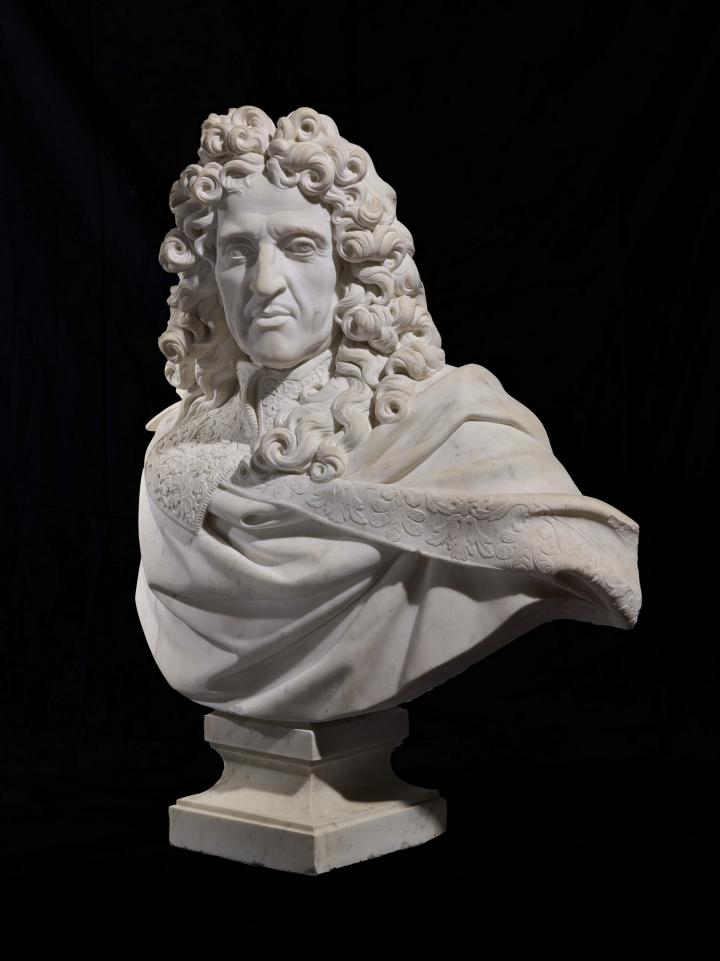
Le Nôtre worked in the service of the monarchy from 1635, starting his career as gardener to Gaston, Duke of Orléans, Louis XIV’s uncle. Born into a family that had been gardeners to the king since the 16th century, he trained in the garden of Les Tuileries (where he received the position of head gardener in 1637, after his father) which he modified in 1666-1672, creating the vast Champs-Elysées perspective. His work in 1656-1661 for Fouquet at Vaux-le-Vicomte earned him fame and fortune.
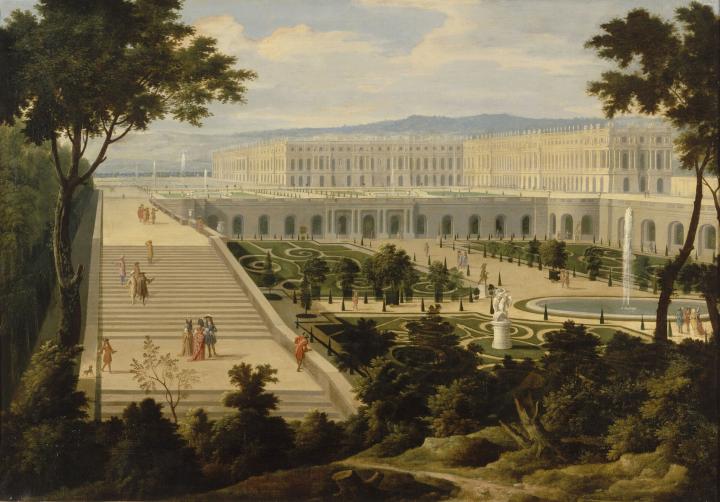
Made Controller General of Buildings to the King in 1657, five years later, as he was working on the gardens of Chantilly for the Grand Condé, he was summoned to Versailles by Louis XIV. From the initial garden left by Louis XIII Le Nôtre created two large parterres to the north and south near the Palace and redesigned the large east-west axis, which he extended into a perspective stretching as far as the eye could see. Although he kept the natural slope of the ground, the rest was redesigned and transformed by labourers.
The landscape gardener made full use of all the water sources and played with light and shade by creating shady spaces (groves) alongside lighter areas (parterres).
Le Nôtre perfected his garden designs in Versailles, using main axes interspersed with secondary alleys marking off the groves. Trellises and arbours formed walls of greenery that strengthened perspectives, while diagonal or winding alleys led to groves designed to surprise visitors. Innovative decor and water features contrasted with the strict symmetry of sections planted with trees.
The landscape gardener made full use of all the water sources and played with light and shade by creating shady spaces (groves) alongside lighter areas (parterres).The parterres and principle alleys were punctuated with statues and yew trees trimmed into surprising forms, making Versailles famous for its topiary art.
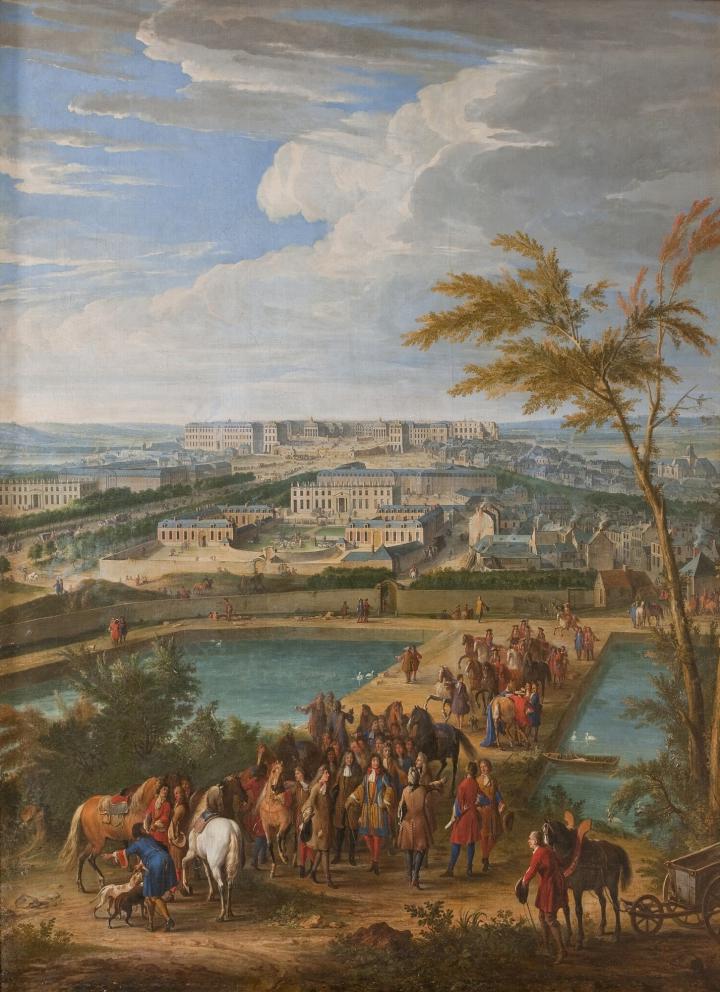
This skilful balance between the symmetry of straight paths and the fantastical design of planted spaces was more or less closely applied in the gardener’s other major creations, such as Saint-Cloud for Monsieur, Louis XIV’s brother (1665), Sceaux for Colbert (1670-77), and Clagny for Madame de Montespan (1674). Besides Versailles, Le Nôtre also designed the large terrace of Saint-Germain (1669-72) and the gardens of Trianon (1672-88) for the king. He was given a title in 1675 and enjoyed not only the king’s favour but also his friendship – something that was extremely rare – until the end. In return, the artist bequeathed him part of his collections in 1693.